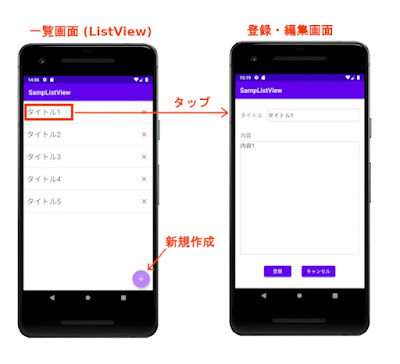
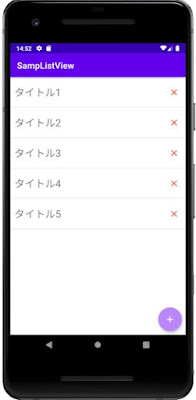
Android Studioで、SQLiteデータベースのデータをListViewに一覧表示し、そのデータを編集・削除する方法を紹介します。
今回作成するのは、SQLiteデータベースの内容をListViewに一覧表示する画面と、データを登録・編集をする画面です。
一覧表示画面 右下の[+]ボタンをタップすると登録画面が表示され、 [登録] ボタンでデータを登録します。
リストをタップすると編集画面が表示されて、データの更新ができます。
リスト右側の × (削除) ボタンをタップすると、データベースのデータが削除されます。
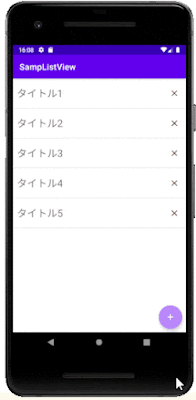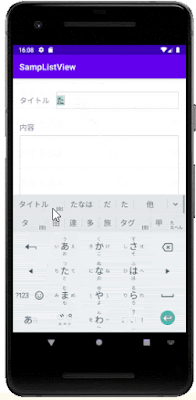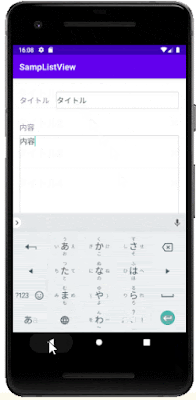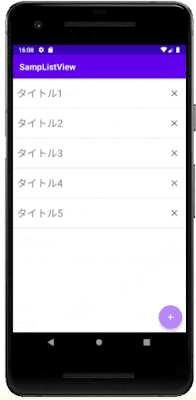
このシンプルなアプリを題材に、データベースの情報をListViewに表示する方法やListViewに配置したボタンによる削除の方法を紹介します。
Android Studioのインストール方法と簡単な使い方については、こちらの記事で紹介しています。
構成
オブジェクトの構成は、このようになっています。
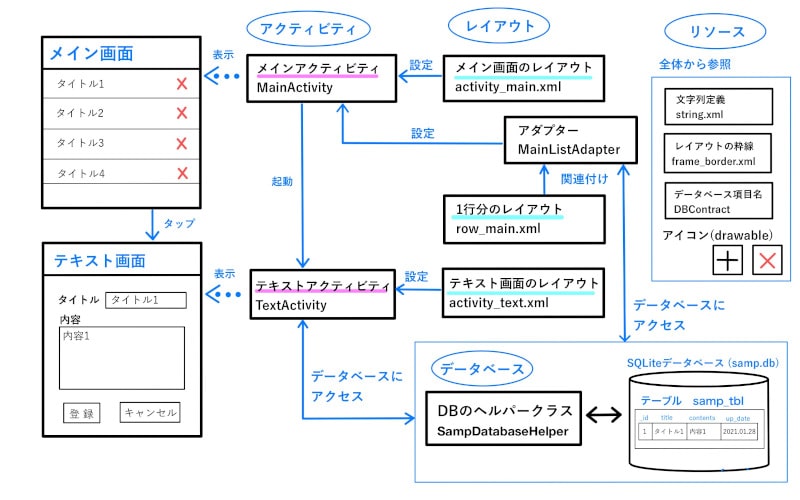
メインアクティビティ(MainActivity)は、メイン画面のレイアウト(activity_main.xml)を使ってメイン画面を表示します。
このメイン画面のレイアウト(activity_main.xml)は、1行分のレイアウト(row_main.xml)とデータベースのデータを関連付けたアダプター(MainListAdapter)によって設定されます。
テキストアクティビティ(TextActivity)は、テキスト画面のレイアウト(activity_text.xml)を使ってテキスト画面を表示します。
データベースへは、データベースヘルパー(SampDatabaseHelper)クラスを経由してアクセスしています。
表示に使用する文字列やデータベースの項目名などは、リソースに定義しているstrings.xmlなどを参照します。
追加ボタンの「+」や削除ボタンの「×」アイコンは、drawable に追加して使用します。
順を追って、詳しく説明していきます。
プロジェクト作成
「Android Studioをインストール」の「プロジェクト作成」で紹介した手順で、プロジェクトを作成します。
プロジェクト名は、 「SampListView」 としました。
リソース準備
アプリ内から参照する次のリソースを準備します。
strings.xml
アプリ内で使用する文字列の定義をします。
app/res/vlues/strings.xml を開いて、次の内容に編集します。
<resources>
<string name="app_name">SampListView</string>
<string name="title">タイトル</string>
<string name="contents">内容</string>
<string name="reg">登録</string>
<string name="del">削除</string>
<string name="cancel">キャンセル</string>
</resources>定義したnameを指定して、プログラムやレイアウトから参照します。
次のファイルは、前回の記事「Android Studio SQLiteデータベースに保存する方法 (TextView・EditText)」と同じです。
- frame_border.xml(タイトルなどの入力欄に枠線を表示)
- DBContract(データベースのテーブル名や項目名を定義)
- SampDatabaseHelper(データベースヘルパークラス)
それぞれ記事内のframe_border.xmlとDBContract、SampDatabaseHelperの部分を参照してください。
アイコン
プロジェクトで使用するアイコンを追加します。
アイコン追加
res/drawable/ で右ボタンをクリックし、 [New] - [Vector Assert] をクリックします。
「Clip Art」の所をクリックします。
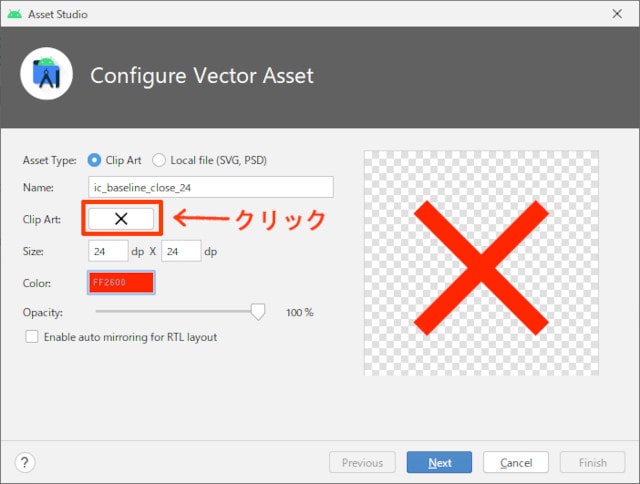
Android Studioにあらかじめ用意されているアイコンが表示されますので、追加したいアイコンを選択します。

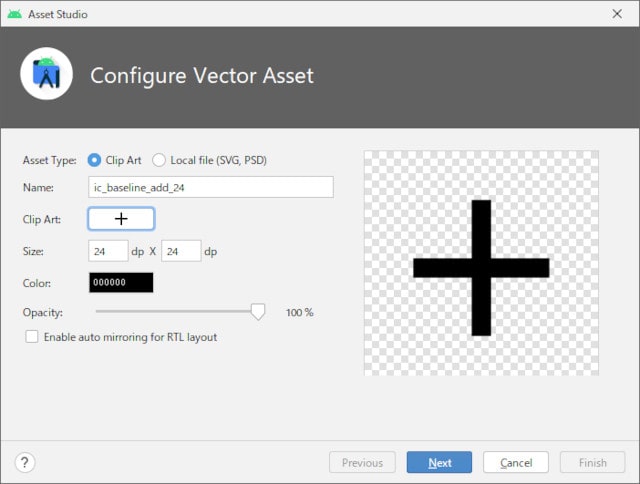
色を赤に変更して、[Next] - [Finish] ボタンをクリックします。
プラスアイコンも同様です。
Gradleのファイルに設定を追加
アイコンが使えるように、次の1行を Gradle Scripts/build.gradle(Module) の defaultConfig に追加します。
・・・
defaultConfig {
vectorDrawables.useSupportLibrary = true
データベース作成
データベースも、前回の記事「【Android】SQLiteデータベースに保存する方法 (TextView・EditText)」と同じです。
記事内のデータベース作成の部分を参照してください。

画面レイアウト
activity_main.xml
app/res/values/activity_main.xml に、メイン画面のレイアウトを設定します。
activity_main.xml(クリックして表示)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/mainList"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<com.google.android.material.floatingactionbutton.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/fab_reg"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:focusable="true"
android:clickable="true"
android:contentDescription="@string/reg"
android:onClick="fab_reg_onClick"
app:srcCompat="@drawable/ic_baseline_add_24"
app:tint="@color/white"
app:backgroundTint="@color/purple_200"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>前回は、縦や横にウィジェットを並べるシンプルな LinearLayout というレイアウトを使用しましたが、今回はConstraintLayout というレイアウトを使用します。
ConstraintLayoutとは
ConstraintLayout は、配置したウィジェットの上下左右など必要な部分に相対的な位置情報(制約)を設定するレイアウトです。
たとえば、「タイトル」というラベル用のTextView の16dp右に、タイトル入力用のEditTextを配置するといった指定をします。
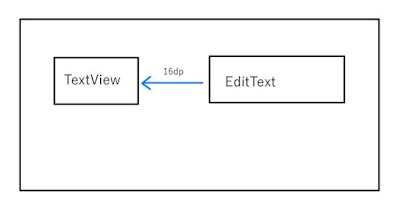
レイアウトエディタで設定すると、視覚的にも理解しやすいです。
右と下に制約をつけると右下に配置され、上下左右に制約をつけると中央に配置されます。
layout_width=”0dp” とすると、ウィジェットがレイアウトいっぱいに広がります。
このソースでは、 ConstraintLayout の画面に ListView と FloatingActionButton を配置しています。
FloatingActionButton
FloatingActionButton(フローティング操作ボタン)というのは、右下に表示している [+] ボタンのことです。
アプリでメインとなる操作を、このように円形のボタンで表示します。
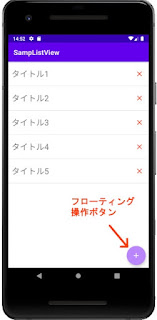
このソースでは、onClick=”fab_reg_onClick” とすることで、クリックされたときにMainActivityの 「fab_reg_onClick()」メソッドを呼んで、登録画面を表示します。
ウィジェットに付与する onClick 属性は、Clickイベントでのみ使える特殊な方法です。
よく利用されるので、このような簡易手段が用意されています。
ListView
ListViewは、データをリスト表示できるウィジェットです。
リストの1行分のフォーマットは、 row_main.xml で定義しています。
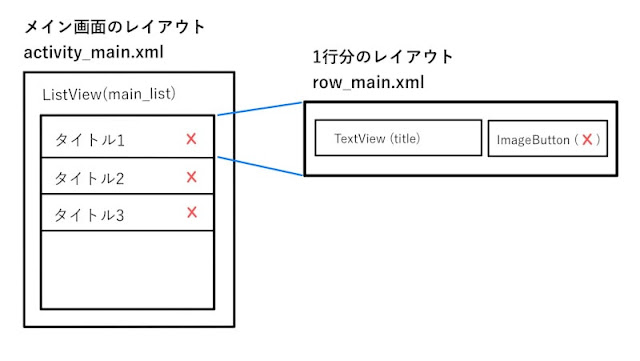
row_main.xml
row_main.xml の内容はこちらです。
row_main.xml(クリックして表示)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:descendantFocusability="blocksDescendants">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="360dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:paddingLeft="10dp"
android:paddingRight="10dp"
android:textSize="24sp" />
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/button_delete"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
android:background="#00000000"
android:contentDescription="@string/del"
android:gravity="center_horizontal|center_vertical"
android:onClick="btnDel_onClick"
app:srcCompat="@drawable/ic_baseline_close_24" />
</LinearLayout>タイトルを表示する TextView と削除用の ImageButton を配置しています。
ListViewにImageButtonを設置すると、ListViewの OnitemClickListener と ButtonのOnClickListener が競合してイベントがとれなくなります。
この状態を回避するため、LinearLayoutの属性に
android:descendantFocusability=”blocksDescendants” を設定しています。
ImageButton に onClick=”btnDel_onClick” を設定しているので、クリックされたときにMainActivityの「btnDel_onClick()」メソッド呼んで削除処理を行います。
activity_text.xml
登録・編集用の画面です。こちらも ConstraintLayout で作成しました。
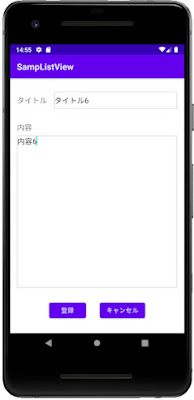
activity_text.xml (クリックして表示)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textTitle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:text="@string/title"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf="@+id/editTitle"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/editTitle"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editTitle"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="16dp"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="32dp"
android:background="@drawable/frame_border"
android:hint="@string/title"
android:importantForAutofill="no"
android:inputType="text"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/textTitle"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textContents"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="40dp"
android:text="@string/contents"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/textTitle" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editContents"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="360dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="16dp"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:background="@drawable/frame_border"
android:gravity="start|top"
android:importantForAutofill="no"
android:inputType="textMultiLine"
android:labelFor="@id/textContents"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="1.0"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/textContents" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_reg"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="16dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="16dp"
android:layout_marginStart="100dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:onClick="btnReg_onClick"
android:text="@string/reg"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/btn_cancel"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/editContents" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_cancel"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="16dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="100dp"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:onClick="btnCancel_onClick"
android:text="@string/cancel"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/btn_reg"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/editContents" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf=”@+id/editTitle” とすることで、タイトルのラベルと入力欄のベースラインを合わせています。
マニフェストファイル
こちらの画面を呼べるように、マニフェストファイル(AndroidManifest.xml)に次の記述を追記します。
<activity android:name=".TextActivity">
</activity>アダプター(Adapter)
アダプター(Adapter)とは、データとウィジェットを関連付け、橋渡しをしてくれるオブジェクトです。
アダプターには、配列データを扱うArrayAdapterや、mapデータを扱うSimpleAdapterなどいろいろな種類があります。
今回のアプリでは、SimpleCursorAdapterを継承してMainListAdapterというアダプターを作成しました。
SimpleCursorAdapterは、カーソル(データベースの検索結果を保持)を渡すことで、ListViewの1行分のレイアウト(row_main.xml)に、データを関連付けてくれるアダプターです。
このMainListAdapterの中で、リストの何行目かという位置情報のタグを各行の削除ボタンに付加しています。
SimpleCursorAdapterに渡すカーソルに、「_id」という名前の列が含まれていないとエラーになってしまいますので注意してください。
MainListAdapter (クリックして表示)
package com.ma_chanblog.samplistview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ImageButton;
import android.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
public class MainListAdapter extends SimpleCursorAdapter {
// コンストラクタ
public MainListAdapter(Context context, int layout, Cursor c, String[] from, int[] to, int flags) {
super(context, layout, c, from, to, flags);
}
// 指定データのビューを取得
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
View view = super.getView(position, convertView, parent);
// 削除ボタン オブジェクトを取得
ImageButton btnDel = (ImageButton) view.findViewById(R.id.button_delete);
// ボタンにリスト内の位置を設定
btnDel.setTag(position);
return view;
}
}アクティビティ
メインアクティビティ
ちょっと長いですが、メイン画面を表示する MainActivity です。
MainActivity(クリックして表示)
package com.ma_chanblog.samplistview;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import static com.ma_chanblog.samplistview.DBContract.DBEntry;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private SampDatabaseHelper helper = null;
MainListAdapter sc_adapter;
// アクティビティの初期化処理
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
// アクティビティの再開処理
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
// データを一覧表示
onShow();
}
// データを一覧表示
protected void onShow() {
// データベースヘルパーを準備
helper = new SampDatabaseHelper(this);
// データベースを検索する項目を定義
String[] cols = {DBEntry._ID, DBEntry.COLUMN_NAME_TITLE, DBEntry.COLUMN_NAME_CONTENTS };
// 読み込みモードでデータベースをオープン
try (SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getReadableDatabase()){
// データベースを検索
Cursor cursor = db.query(DBEntry.TABLE_NAME, cols, null,
null, null, null, null, null);
// 検索結果から取得する項目を定義
String[] from = {DBEntry.COLUMN_NAME_TITLE};
// データを設定するレイアウトのフィールドを定義
int[] to = {R.id.title};
// ListViewの1行分のレイアウト(row_main.xml)と検索結果を関連付け
sc_adapter = new MainListAdapter(
this, R.layout.row_main, cursor, from, to,0);
// activity_main.xmlに定義したListViewオブジェクトを取得
ListView list = findViewById(R.id.mainList);
// ListViewにアダプターを設定
list.setAdapter(sc_adapter);
// リストの項目をクリックしたときの処理
list.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
public void onItemClick(AdapterView av, View view, int position, long id) {
// クリックされた行のデータを取得
Cursor cursor = (Cursor)av.getItemAtPosition(position);
// テキスト登録画面 Activity へのインテントを作成
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, com.ma_chanblog.samplistview.TextActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(DBEntry._ID, cursor.getInt(0));
intent.putExtra(DBEntry.COLUMN_NAME_TITLE, cursor.getString(1));
intent.putExtra(DBEntry.COLUMN_NAME_CONTENTS, cursor.getString(2));
// アクティビティを起動
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
// 削除ボタン タップ時に呼び出されるメソッド
public void btnDel_onClick(View view){
// MainListAdapterで設定されたリスト内の位置を取得
int pos = (Integer)view.getTag();
// アダプターから、_idの値を取得
int id = ((Cursor) sc_adapter.getItem(pos)).getInt(0);
// データを削除
try (SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase()) {
db.delete(DBEntry.TABLE_NAME, DBEntry._ID+" = ?", new String[] {String.valueOf(id)});
}
// データを一覧表示
onShow();
}
// 「+」フローティング操作ボタン タップ時に呼び出されるメソッド
public void fab_reg_onClick(View view) {
// テキスト登録画面 Activity へのインテントを作成
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, com.ma_chanblog.samplistview.TextActivity.class);
// アクティビティを起動
startActivity(intent);
}
}onResume()
これまで使用してきたonCreate() メソッドは、アクティビティが開始されたときに、初期化処理として実行されるメソッドです。
今回は、メインの一覧画面から登録・編集画面を呼び出し、またメインの画面が復帰する流れになるため、フォアグラウンドになるときに呼び出されるonResume()メソッドでも、画面の再表示を行っています。
onCreate()やonResume()のようなアクティビティのライフサイクルについては、公式サイトで紹介されています。
インテント(Intent)
インテントは、他のアクティビティに情報を受け渡すための入れ物(非同期メッセージ)です。
今回のアプリでは、MainActivityでリストがクリックされたときに、クリックされた行のIDやタイトルなどの情報をインテントにつめてTextActivity に送っています。
テキストアクティビティ
登録・編集用の画面を表示するテキストアクティビティです。
TextActivity(クリックして表示)
package com.ma_chanblog.samplistview;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import static com.ma_chanblog.samplistview.DBContract.DBEntry;
public class TextActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private int id = 0;
private EditText editTitle = null;
private EditText editContents = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_text);
// ビューオブジェクトを取得
editTitle = findViewById(R.id.editTitle);
editContents = findViewById(R.id.editContents);
// インテントを取得
Intent intent = getIntent();
//intentのデータを取得(データがない場合、第2引数の 0 が返る)
id = intent.getIntExtra(DBEntry._ID,0);
String title = intent.getStringExtra(DBEntry.COLUMN_NAME_TITLE);
String contents = intent.getStringExtra(DBEntry.COLUMN_NAME_CONTENTS);
// データ更新の場合
if (id > 0){
editTitle.setText(title);
editContents.setText(contents);
}
}
// 「登録」ボタン タップ時に呼び出されるメソッド
public void btnReg_onClick(View view) {
// ヘルパーを準備
SampDatabaseHelper helper = new SampDatabaseHelper(this);
// 入力欄に入力されたタイトルとコンテンツを取得
String title = editTitle.getText().toString();
String contents = editContents.getText().toString();
// 書き込みモードでデータベースをオープン
try (SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase()) {
// 入力されたタイトルとコンテンツをContentValuesに設定
// ContentValuesは、項目名と値をセットで保存できるオブジェクト
ContentValues cv = new ContentValues();
cv.put(DBEntry.COLUMN_NAME_TITLE, title);
cv.put(DBEntry.COLUMN_NAME_CONTENTS, contents);
if(id == 0) {
// データ新規登録
db.insert(DBEntry.TABLE_NAME, null, cv);
} else {
// データ更新
db.update(DBEntry.TABLE_NAME, cv, DBEntry._ID + " = ?", new String[] {String.valueOf(id)});
}
}
// TextActivityを終了
finish();
}
// 「キャンセル」ボタン タップ時に呼び出されるメソッド
public void btnCancel_onClick(View view) {
// TextActivityを終了
finish();
}
}まとめ
Android Studioで、SQLiteデータベースのデータをListViewで一覧表示する方法を紹介しました。
また、Intentを使ってサブ画面に情報を送る方法や、削除アイコンをタップしてデータベースのデータを削除する一連の動作が確認できたと思います。
いろいろカスタマイズして、独自のリストを作ってみるのもおもしろいと思います。
次回は、別の一覧表示の方法を紹介します。